들어가며
트랜잭션 경합이 빈번하거나 분산 환경에서 동시성 문제가 발생할 수 있는 상황에서,
RDB에 의존하는 낙관적 락 대신 독립적인 외부 분산 락 시스템을 사용하는 것에 관심이 생겼다.
이번 기회에 정리하며 적용해보고자 한다.
Redisson의 장점
- Redis 클러스터, Sentinel 환경과의 호환성까지 갖춰 운영 환경에서도 안정적으로 사용할 수 있다.
- Java 생태계에 친화적이며, elasticcache 등 redis 인프라가 이미 구축된 경우 쉽게 확장 가능하다.
- Lettuce, Jedis보다는 RLock, RReadWriteLock, RedLock, Watchdog(락 재연장) 등 제공하는 기능이 다양하다.
Redisson 구조
Redisson Lock 종류
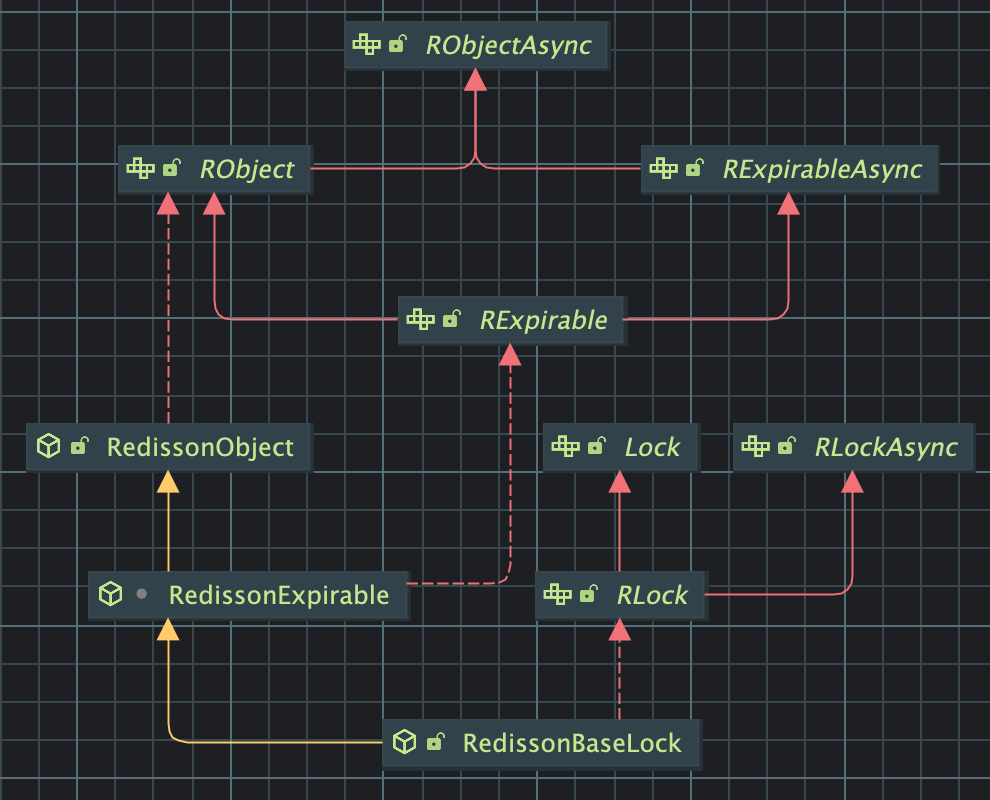
Redisson에 사용되는 락 종류는 가장 하단 추상 클래스인 RedissonBaseLock을 구현하는 구조이다.
RedissonBaseLock의 종류들에 대해 간단히 알아보자

| RedissonLock | 기본 분산 락 - 가장 많이 사용되는 일반 락 |
| RedissonFairLock | 공정 락(Fair Lock) 락 요청 순서(FIFO) 보장 |
| RedissonFencedLock | 펜스 락(Fenced Lock) 버전 넘버를 반환해, 장애 상황에서도 중복 작업 방지 주로 마이크로서비스, DB 연동 시 사용 |
| RedissonSpinLock | 스핀 락(Spin Lock) 락이 풀릴 때까지 계속 빠르게 재시도 CPU 사용량 높음 |
| RedissonReadLock | 읽기 락(Read Lock) 여러 쓰레드가 동시에 읽기 가능 쓰기 작업은 차단됨 |
| RedissonWriteLock | 쓰기 락(Write Lock) 데이터 수정 시 사용 배타적 락 |
| RedissonTransactionalLock | 트랜잭션 락 Redisson의 트랜잭션 기능과 결합 |
| RedissonTransactionalReadLock | Redisson 트랜잭션 환경에서 사용하는 읽기 락 |
| RedissonTransactionalWriteLock | Redisson 트랜잭션 환경에서 사용하는 쓰기 락 |
Redisson 동작 과정
RedissonClient에서 lock 을 수행하는 메서드를 살짝 뜯어보도록 한다.
tryLock
- 락 취득에 성공했을 때는 true를 반환
- 락 취득 실패 시 Pub/Sub 채널을 구독하여 락 상태에 대해 확인
- 만일 락 해제 알림을 수신 시 락 점유 재시도
waitTime, leaseTime, unit등을 파라미터로 갖고 있는 것을 기억하자
boolean tryLock (링크)
public boolean tryLock(long waitTime, long leaseTime, TimeUnit unit) throws InterruptedException {
long time = unit.toMillis(waitTime);
long current = System.currentTimeMillis();
long threadId = Thread.currentThread().getId();
Long ttl = this.tryAcquire(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId);
// lock acquired
if (ttl == null) {
return true;
} else {
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current;
if (time <= 0L) {
this.acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;
} else {
current = System.currentTimeMillis();
CompletableFuture<RedissonLockEntry> subscribeFuture = this.subscribe(threadId);
try {
subscribeFuture.get(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} catch (TimeoutException var21) {
if (!subscribeFuture.completeExceptionally(new RedisTimeoutException("Unable to acquire subscription lock after " + time + "ms. Try to increase 'subscriptionsPerConnection' and/or 'subscriptionConnectionPoolSize' parameters."))) {
subscribeFuture.whenComplete((res, ex) -> {
if (ex == null) {
this.unsubscribe(res, threadId);
}
});
}
this.acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;
} catch (ExecutionException var22) {
this.acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
return false;
}
try {
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - current;
if (time <= 0L) {
this.acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
boolean var24 = false;
return var24;
} else {
boolean var16;
do {
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
ttl = this.tryAcquire(waitTime, leaseTime, unit, threadId);
if (ttl == null) {
var16 = true;
return var16;
}
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;
if (time <= 0L) {
this.acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
var16 = false;
return var16;
}
currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
if (ttl >= 0L && ttl < time) {
((RedissonLockEntry)this.commandExecutor.getNow(subscribeFuture)).getLatch().tryAcquire(ttl, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
} else {
((RedissonLockEntry)this.commandExecutor.getNow(subscribeFuture)).getLatch().tryAcquire(time, TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
}
time -= System.currentTimeMillis() - currentTime;
} while(time > 0L);
this.acquireFailed(waitTime, unit, threadId);
var16 = false;
return var16;
}
} finally {
this.unsubscribe((RedissonLockEntry)this.commandExecutor.getNow(subscribeFuture), threadId);
}
}
}
}
subscribe (org.redisson.pubsub.PublishSubscribe)
protected CompletableFuture<RedissonLockEntry> subscribe(long threadId) {
return this.pubSub.subscribe(this.getEntryName(), this.getChannelName());
}public CompletableFuture<E> subscribe(String entryName, String channelName) {
// redisson library의 커스텀 completableFuture 슬롯 중 하나를 불러옴
AsyncSemaphore semaphore = this.service.getSemaphore(new ChannelName(channelName));
CompletableFuture<E> newPromise = new CompletableFuture();
// 기존 세마포어에서 대기 큐의 completeablefuture를 소진한 후 새로운 completeablefuture를 반환
semaphore.acquire().thenAccept((c) -> {
// newPromise가 이미 완료된 경우 세마포어 반환 후 종료
if (newPromise.isDone()) {
semaphore.release();
} else {
E entry = (PubSubEntry)this.entries.get(entryName);
if (entry != null) { // 기존 엔트리 존재
entry.acquire();
semaphore.release();
entry.getPromise().whenComplete((r, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
newPromise.completeExceptionally(e);
} else {
newPromise.complete(r);
}
});
} else { // 새로운 엔트리 생성 (최초 구독 시도)
E value = this.createEntry(newPromise);
value.acquire();
E oldValue = (PubSubEntry)this.entries.putIfAbsent(entryName, value);
if (oldValue != null) { // 기존 엔트리 존재 시 기존 엔트리 재사용
oldValue.acquire();
semaphore.release();
oldValue.getPromise().whenComplete((r, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
newPromise.completeExceptionally(e);
} else {
newPromise.complete(r);
}
});
} else { // 최초 등록된 경우: Redis Pub/Sub 리스너 생성 및 구독 요청
RedisPubSubListener<Object> listener = this.createListener(channelName, value);
CompletableFuture<PubSubConnectionEntry> s = this.service.subscribeNoTimeout(LongCodec.INSTANCE, channelName, semaphore, new RedisPubSubListener[]{listener});
newPromise.whenComplete((r, e) -> {
if (e != null) {
s.completeExceptionally(e);
}
});
// 구독 완료 / 실패 처리
s.whenComplete((r, e) -> {
if (e != null) { // 예외 발생하며 종료
this.entries.remove(entryName);
value.getPromise().completeExceptionally(e);
} else { // 완전한 종료
value.getPromise().complete(value);
}
});
}
}
}
});
return newPromise;Spring + Redisson 적용
백문이 불여일타.. ⌨️
간단한 재고 업데이트에 데이터 정합성을 지키기 위한 락을 Redisson을 이용해 부여해보자.
Redisson이 제공 하는 락 중 기본 락인 RedissonLock을 사용하였다.
RedissonLock은 비공정 락이기 때문에, 동시다발적인 요청이 들어와도 순차 처리는 보장되지 않는다.
만일 순서를 보장하고 싶다면, 공정 락인 RedissonFairLock을 사용하도록 하자 😊
구현 환경
Spring Boot 3.4.4
JDK 17
build.gradle 의존성 등록
redisson과 spring data redis(선택) 의 의존성을 추가해주자.
dependencies {
implementation 'org.redisson:redisson:3.22.0'
implementation 'org.springframework.boot:spring-boot-starter-data-redis'
}
application.yml
spring:
data:
redis:
host: localhost
port: 6380 # 기본은 6379, 환경에 맞출 것
RedissonClient 설정
redisson을 사용하기 위한 connection 정보를 설정한다.
spring data redis를 사용하고 있었기 때문에 host, port 프로퍼티를 재활용했다.
@Configuration
public class RedissonConfig {
@Value("${spring.data.redis.host}") // spring data redis 의 설정을 재사용
private String redisHost;
@Value("${spring.data.redis.port}")
private int redisPort;
private static final String REDISSON_HOST_PREFIX = "redis://";
@Bean
public RedissonClient redissonClient() {
Config config = new Config();
config.useSingleServer().setAddress(REDISSON_HOST_PREFIX + redisHost + ":" + redisPort);
return Redisson.create(config);
}
}
커스텀 어노테이션 @RedissonLock 생성
모든 관심사에 redisson lock, unlock 코드를 삽입하는 것은 관리가 어렵다.
lock에 필요한 파라미터를 어노테이션으로 입력받아
| waitTime | 락을 획득 전 최대 대기할 시간 |
| leaseTime | 락 보유 가능 시간 |
| timeUnit | 시간 단위 (ms, s, etc..) |
waitTime을 0으로 지정할 때는 이미 점유된 자원을 취득하기 위해 대기하지 않을 것이고,
waitTime을 0 초과로 설정할 경우에는 대기하면서 락을 취득하려 할 것이다.
@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface RedissonDefaultLock {
String key();
}@Target(ElementType.METHOD)
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface RedissonLock {
String key();
long waitTime() default 1000L;
long leaseTime() default 5000L;
TimeUnit timeUnit() default TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS;
}waittime을 동적 / 고정으로 설정해 주고자 두 가지 어노테이션을 생성했다.
@RedissonLock Aspect 등록
어노테이션 전후로 실질적인 락 등록과 해제를 수행하는 로직을 포함하는 Aspect
@Slf4j
@Aspect
@Component
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class RedissonLockAspect {
private final RedissonClient redissonClient;
private final SpelExpressionParser parser = new SpelExpressionParser();
private final DynamicLockConfig dynamicLockConfig;
/**
* bean config로 동적으로 time을 조절 가능한 aspect
*/
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.soi.redisson.annotation.RedissonLock)")
public void redissonLockPointcut() {
}
/**
* properties로 고정된 waittime, leasetime을 가지는 aspect
*/
@Pointcut("@annotation(com.soi.redisson.annotation.RedissonDefaultLock)")
public void redissonDefaultLockPointcut() {
}
@Around("redissonLockPointcut() && @annotation(redissonLock)")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, RedissonLock redissonLock) throws Throwable {
String key = parseKey(joinPoint, redissonLock.key());
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock(key);
boolean locked = false;
try {
locked = lock.tryLock(redissonLock.waitTime(), redissonLock.leaseTime(), redissonLock.timeUnit());
if (!locked) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to acquire lock for key: " + key);
}
Object result = joinPoint.proceed();
handleUnlock(lock);
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
safeUnlock(lock, locked);
throw e;
}
}
@Around("redissonDefaultLockPointcut() && @annotation(redissonDefaultLock)")
public Object around(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, RedissonDefaultLock redissonDefaultLock) throws Throwable {
String key = parseKey(joinPoint, redissonDefaultLock.key());
RLock lock = redissonClient.getLock(key);
boolean locked = false;
try {
locked = lock.tryLock(dynamicLockConfig.getWaitTime(), dynamicLockConfig.getLeaseTime(), TimeUnit.MILLISECONDS);
if (!locked) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to acquire lock for key: " + key);
}
Object result = joinPoint.proceed();
handleUnlock(lock);
return result;
} catch (Exception e) {
safeUnlock(lock, locked);
throw e;
}
}
/**
* @param lock
* commit 후 unlock
*/
private void handleUnlock(RLock lock) {
if (TransactionSynchronizationManager.isSynchronizationActive()) {
TransactionSynchronizationManager.registerSynchronization(new TransactionSynchronization() {
@Override
public void afterCommit() {
TransactionSynchronization.super.afterCommit();
lock.unlock();
}
});
} else {
safeUnlock(lock, true);
}
}
private void safeUnlock(RLock lock, boolean locked) {
if (locked && lock.isHeldByCurrentThread()) {
lock.unlock();
}
}
private String parseKey(ProceedingJoinPoint joinPoint, String key) {
MethodSignature signature = (MethodSignature) joinPoint.getSignature();
EvaluationContext context = new StandardEvaluationContext();
String[] paramNames = signature.getParameterNames();
Object[] args = joinPoint.getArgs();
for (int i = 0; i < paramNames.length; i++) {
context.setVariable(paramNames[i], args[i]);
}
return parser.parseExpression(key).getValue(context, String.class);
}
}
Service 등록
재고를 업데이트하는 간단한 서비스 레이어 (StockService 인터페이스는 생략)
@Service
@Slf4j
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class StockServiceImpl implements StockService {
private final StockRepository stockRepository;
@Override
@Transactional
@RedissonLock(key = "'lock:product:' + #stockId")
public void updateStock(Long stockId, Long offset) {
log.info("stock update");
Stock stock = stockRepository.findById(stockId).orElseThrow();
if (stock.getCount() + offset < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
stock.updateStock(offset);
}
@Override
@Transactional
@RedissonDefaultLock(key = "'lock:product:' + #stockId")
public void updateStockDefault(Long stockId, Long offset) {
log.info("stock update default");
Stock stock = stockRepository.findById(stockId).orElseThrow();
if (stock.getCount() + offset < 0) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException();
}
stock.updateStock(offset);
}
}
테스트
10명의 유저가 동시에 재고 업데이트를 요청 시 오직 한 명의 유저만이 접근할 수 있는지를 테스트한다.
명확한 테스트를 위해 waitTime을 0으로 설정해둔 상태이다.
@SpringBootTest
@TestInstance(TestInstance.Lifecycle.PER_CLASS)
public class RedissonLockAopTest {
public static final long STOCK_ID = 1L;
@Autowired
private StockService stockService;
@Autowired
private StockRepository stockRepository;
@Autowired
private RedissonClient redissonClient;
@Autowired
private DynamicLockConfig dynamicLockConfig;
@BeforeAll
void init() {
stockRepository.save(new Stock(STOCK_ID, 0L));
}
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
redissonClient.getKeys().flushall();
}
private boolean updateInventory(long offset, AtomicInteger success, AtomicInteger fail) {
try {
stockService.updateStock(STOCK_ID, offset);
success.incrementAndGet();
} catch (Exception e) {
fail.incrementAndGet();
}
return true;
}
private boolean updateInventoryDefault(long offset, AtomicInteger success, AtomicInteger fail) {
try {
stockService.updateStockDefault(STOCK_ID, offset);
success.incrementAndGet();
} catch (Exception e) {
fail.incrementAndGet();
}
return true;
}
@Test
@DisplayName("동시에_요청하지만_하나만_재고변경")
void onlyOneLock() {
dynamicLockConfig.setWaitTime(0L);
stockRepository.save(new Stock(STOCK_ID, 0L));
int threadCount = 10;
List<CompletableFuture<Boolean>> futures = new ArrayList<>();
AtomicInteger success = new AtomicInteger();
AtomicInteger fail = new AtomicInteger();
futures.add(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> updateInventoryDefault(1L, success, fail)));
for (int i = 1; i < threadCount; i++) {
futures.add(CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> updateInventoryDefault(1L, success, fail)));
}
CompletableFuture.allOf(futures.toArray(new CompletableFuture[0])).join();
Stock stock = stockRepository.findById(STOCK_ID).orElseThrow();
assertThat(stock.getCount()).isEqualTo(1L);
}
}
마무리
Redisson을 활용하면 분산 환경에서도 간단하게 동시성 문제를 해결할 수 있다.
분산 시스템에서는 책임을 적절한 인프라나 모듈로 위임하는 전략이 핵심이다.
이번 Redisson 적용 사례처럼, 동시성 제어의 책임을 Redis로 위임함으로써 애플리케이션/DB 레이어의 부담을 줄일 수 있었다.
물론, 다양한 외부 자원을 활용할수록 관리 포인트는 늘어나게 된다.
하지만 각 컴포넌트의 책임이 명확해지기 때문에, 시스템의 수평적 확장(Scaling Out) 에는 오히려 더 유리한 구조를 만들 수 있다.
결국 이러한 트레이드오프를 잘 이해하고, 상황에 맞는 최적의 기술을 선택하는 것이 중요하겠다.
참고
https://github.com/redisson/redisson
